Options
align
To show all available options and their default values you can type in your terminal:
captus align --help
Input
-e, --captus_extractions_dir
Path to the output directory from the extract command, (e.g. 03_extractions iy you used the default name). The align command depends entirely on the output from the extract step, in other words, you can’t provide your unaligned or aligned FASTA files for processing.
This argument is required , the default is ./03_extractions/
-m, --markers
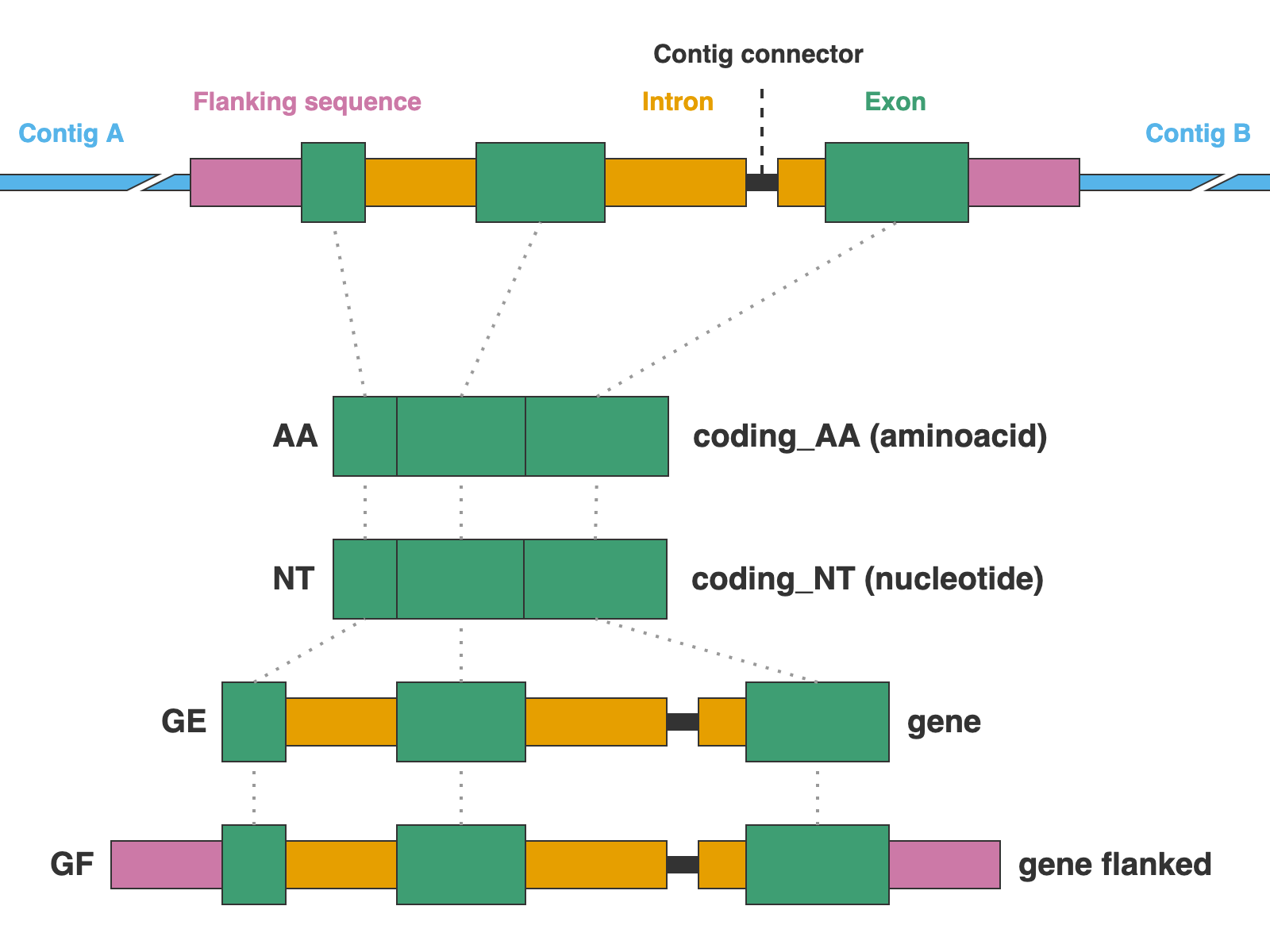
Which type(s) of markers to align, you can provide a comma-separated list (no spaces). These are the available marker types:
NUC= Nuclear proteins inside directories ‘01_coding_NUC’PTD= Plastidial proteins inside directories ‘02_coding_PTD’MIT= Mitochondrial proteins inside directories ‘03_coding_MIT’DNA= Miscellaneous DNA markers inside directories ‘04_misc_DNA’CLR= Cluster-derived DNA markers inside directories ‘05_clusters’ALL= Shortcut for NUC,PTD,MIT,DNA,CLR
This argument is optional, the default is ALL.
-f, --formats
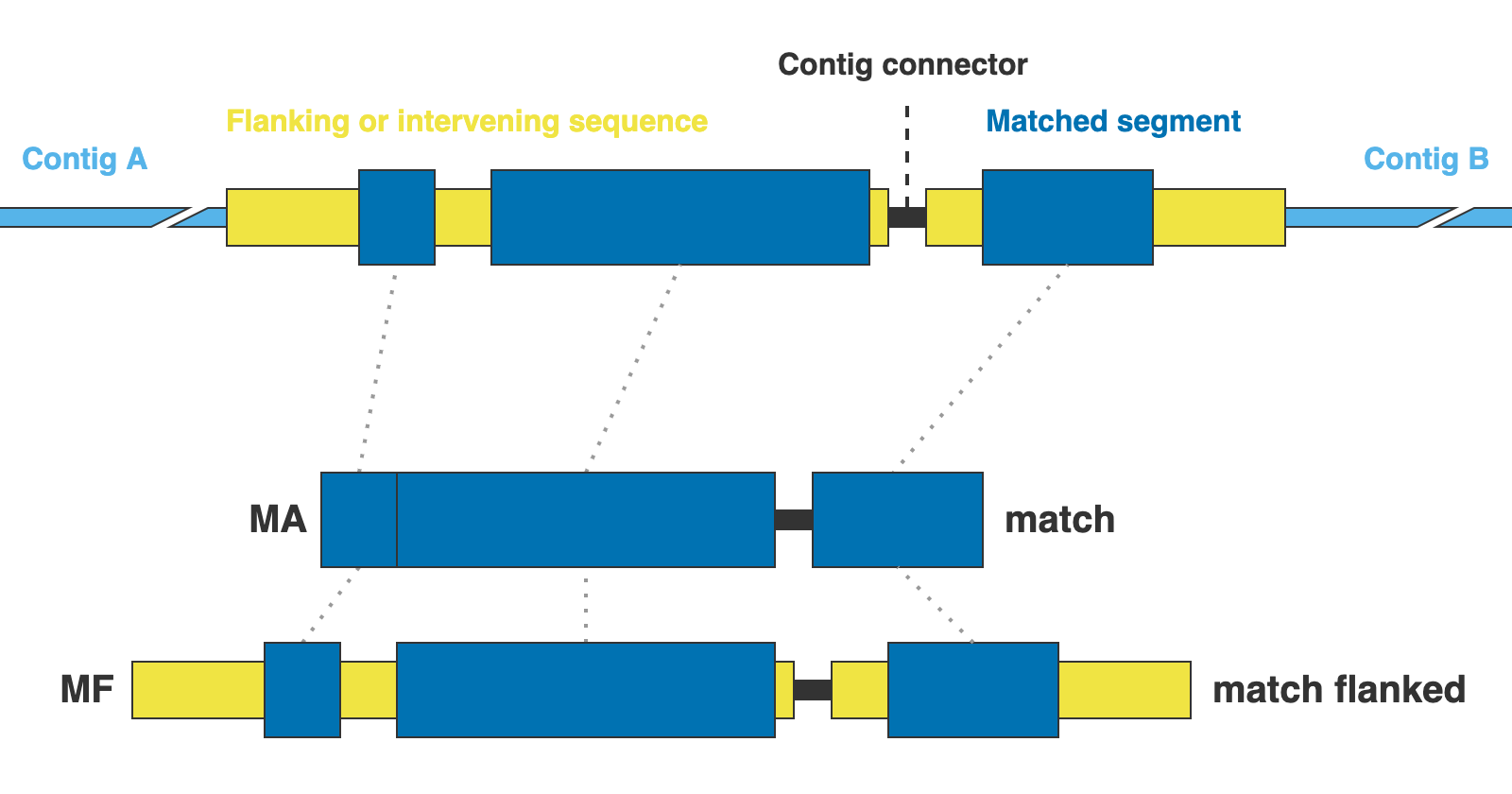
For each marker type, Captus creates several different formats. You can provide a comma-separated list (no spaces) of the formats you wish to align. These are the available formats:
AA= Coding sequences in aminoacidsNT= Coding sequences in nucleotidesGE= Complete gene sequences (exons + introns) without extra flanking sequenceGF= Complete gene sequences with flanking upstream and downstream basepairsMA= Matched sequences without extra flanking sequenceMF= Matched sequences with flanking upstream and downstream basepairsALL= Shortcut for AA,NT,GE,GF,MA,MF
* AA, NT, GE, and GF are valid only for NUC, PTD, and MIT markers, while MA and MF are valid only for DNA and CLR
This argument is optional, the default is AA,NT,GE,MA
--max_paralogs
Maximum number of secondary hits (copies) per sample to import from the extraction step. Large numbers of marker copies per sample can increase alignment times. Hits (copies) are ranked from best to worst during the ’extract’ step. -1 disables the initial removal of paralogs and aligns which might be useful if you expect very high ploidy levels for example.
This argument is optional, the default is 5
-s, --min_samples
Minimum number of samples in a marker to proceed with alignment. Markers with fewer samples will be skipped. The default 4 corresponds to smallest number of sequences to build a rooted phylogeny.
This argument is optional, the default is 4
Output
-o, --out
With this option you can redirect the output directory to a path of your choice, that path will be created if it doesn’t already exist.
This argument is optional, the default is ./04_alignments/
--keep_all
Many intermediate log files are created by MAFFT/MUSCLE and ClipKIT during assembly, Captus deletes all the unnecesary intermediate files unless you enable this flag.
--overwrite
Use this flag with caution, this will replace any previous result within the output directory (for the sample names that match).
Alignment
--align_method
Select the alignment algorithm for MAFFT or MUSCLE 5. Valid algorithm names are:
mafft_auto= MAFFT’s automatic selection based on amount of datamafft_genafpair= MAFFT’s E-INS-i (very slow, multiple conserved domains and long gaps)mafft_localpair= MAFFT’s L-INS-i (very slow, one conserved domain and long gaps)mafft_globalpair= MAFFT’s G-INS-i (very slow, global homology)mafft_retree1= MAFFT’s FFT-NS-1 (fast, progressive method)mafft_retree2= MAFFT’s FFT-NS-2 (very fast, progressive method)muscle_align= MUSCLE 5’s default PPP algorithm (very slow)muscle_super5= MUSCLE 5’s Super 5 algorithm (slow)
This argument is optional, the default is mafft_auto.
--timeout
Modify the waiting time in seconds for an individual alignment to complete. When using more exhaustive MAFFT algorithm (e.g., genafpair) or especially MUSCLE (considerably slower than MAFFT in general), alignment can take very long (up to hours depending on sample number an length of the sequences).
This argument is optional, the default is 21600 (= 6 hours).
--disable_codon_align
When AAs and their corresponding NTs are aligned in the same run, Captus uses the AA alignment as template for aligning the NT format, thus obtaining a codon-aware alignment for the coding sequences in nucleotides. Use this flag to disable this method and use the regular MAFFT/MUSCLE nucleotide alignment.
--outgroup
Outgroup sample names, separated by commas, no spaces. Captus will place these samples whenever possible at the beginning of the alignments, since many phylogenetic programs root the resulting phylogeny at the first sample in the alignment your trees will be automatically rooted.
Example: --outgroup sample2,sample5
This argument is optional and has no default.
Paralog filtering
--filter_method
We provide two filtering methods for paralog removal, you can select either or both:
naive= Only the best hit for each sample (marked as hit=00) is retained.informed= Only keep the copy (regardless of hit ranking) that is most similar to the reference sequence that was chosen most frequently among all other samples in the alignment. This method was designed to take advantage of references that contain several sequences per locus (likeAngiosperms353), if the reference only contains a single reference per locus the result will be very similar to thenaivemethod (see--tolerance).both= Two separate folders will be created, each containing the results from each filtering method.none= Skip paralog removal, just remove reference sequences from the alignments. Useful for phylogenetic methods that allow paralogs likeASTRAL-Pro.
This argument is optional, the default is both.
--tolerance
Only applicable to the informed filter. If the selected copy’s identity to the most commonly chosen reference is below this number of Standard Deviations from the mean, it will also be removed (the lower the number the stricter the filter).
This argument is optional, the default is 2.0.
Trimming (TAPER and ClipKIT)
-c, --taper_cutoff
TAPER cutoff threshold, values greater than 1.0 are recommended, the lower the value the more aggressive the correction, 3.0 recommended by TAPER’s authors.
This argument is optional, the default is 3.0.
--taper_conservative
Enable the more conservative mode of TAPER. Captus uses the aggressive mode by default, see ‘correction_multi_aggressive.jl’ at https://github.com/chaoszhang/TAPER".
--taper_ufiltered
Enable TAPER correction even for alignments than have not been paralog-filtered, TAPER is only able to distinguish error when an unfiltered alignment contains copies of the locus that are not extremely divergent.
--disable_taper
Disable TAPER algorithm for masking for erroneous regions in alignments, see https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13696
--clipkit_method
Select ClipKIT’s trimming mode. Valid trimming modes are:
smart-gapgappykpickpic-smart-gapkpic-gappykpikpi-smart-gapkpi-gappy
This argument is optional, the default is gappy.
-g, --clipkit_gaps
Gappyness threshold per position. Accepted values between 0 and 1. This argument is ignored when using the kpi and kpic algorithms or intermediate steps that use smart-gap.
This argument is optional, the default is 0.9.
-d, --min_data_per_column
Minimum number of non-missing sites per column. When this parameter is > 0, Captus will dynamically calculate a --clipkit_gaps threshold per alignment to keep this minimum amount of data per column.
This argument is optional, the default is 0.
--ends_only
Trim only the ends of the alignments (do not trim internal gaps).
-v, --min_coverage
Minimum coverage of sequence as proportion of the mean of sequence lengths in the alignment, ignoring gaps. After ClipKIT finishes trimming columns, Captus will also remove short sequences below this threshold.
This argument is optional, the default is 0.4.
Other
--collect_only
Only collect the markers from the extraction folder and exit, it skips the addition of reference target sequences and subsequent steps.
--redo_from
You can repeat the analysis without undoing all the steps. These are the points from which you can restart the align command:
alignment= Delete all subdirectories with alignments and restart.filtering= Delete all subdirectories with paralog-filtered alignments and restart.removal= Delete all subdirectories with alignments whose references have been removed and restart.trimming= Delete all subdirectories with trimmed alignments and restart.
This argument is optional and has no default.
--mafft_path, --muscle_path, --clipkit_path
If you have installed your own copies of MAFFT, MUSCLE or ClipKIT you can provide the full path to those copies.
These arguments are optional, the defaults are mafft and clipkit respectively.
--show_less
Enable this flag to show individual alignment information during the run. Detailed information is written regardless to the log.
--ram, --threads, --concurrent, --debug,
See Parallelization (and other common options)
Created by Edgardo M. Ortiz (06.08.2021) Last modified by Edgardo M. Ortiz (09.04.2024)